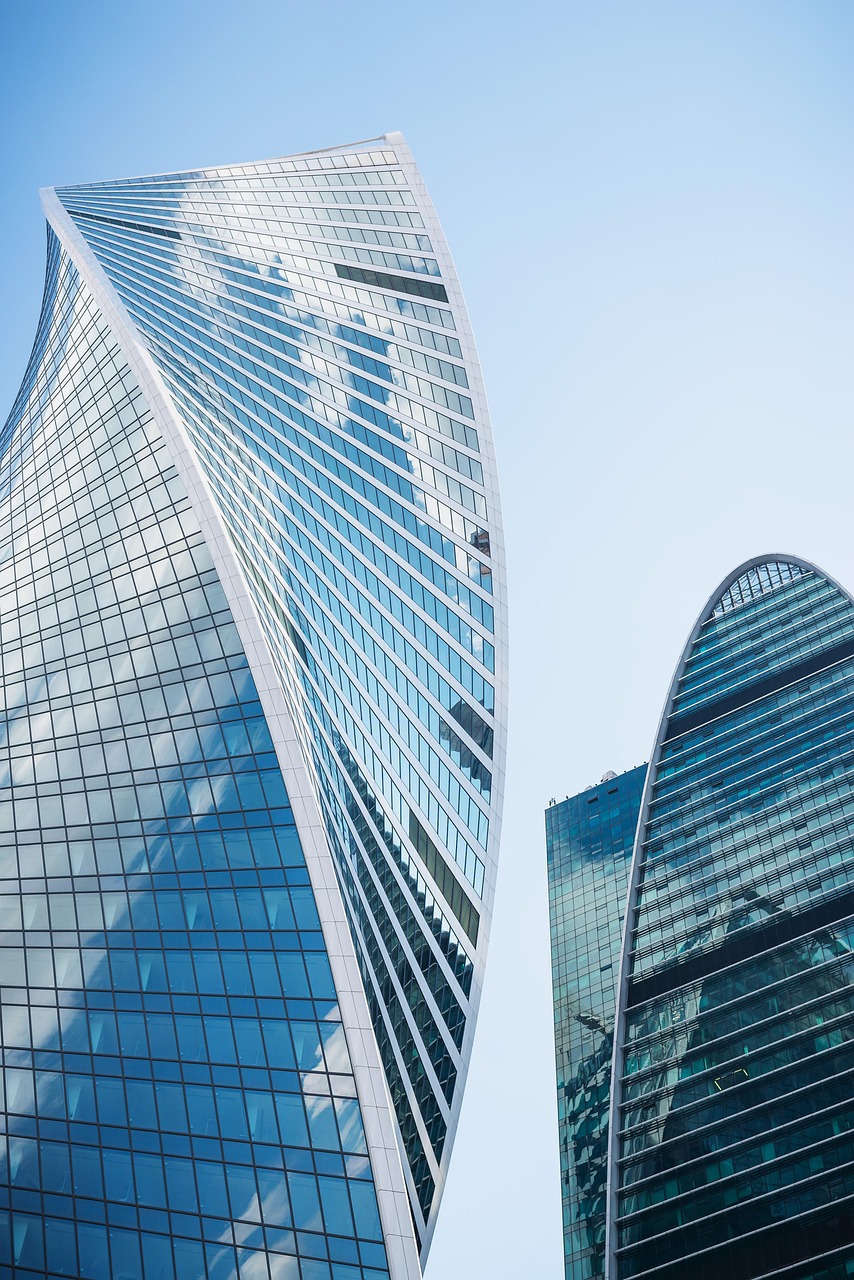
The landscape of architecture is undergoing a profound transformation as designers and engineers embrace innovative approaches to meet the dynamic needs of contemporary society. With a focus on sustainability, technological advancement, and aesthetic innovation, modern architecture is reshaping the way we interact with our environments.

The dawn of the 21st century has heralded a transformative era in the realm of architecture and urban planning, reminiscent of past renaissances that redefined cultural, artistic, and technological paradigms. This period is characterized by an unprecedented fusion of innovation, sustainability, and technology, fundamentally altering how built environments are conceived, constructed, and experienced.
Background
Historical Context and Inspirations
Building upon centuries of architectural evolution, the modern renaissance in design draws inspiration from historical movements such as the Gothic, Baroque, and the original Renaissance, while integrating contemporary technological advancements. The recognition that architecture reflects societal values has driven a shift towards creating spaces that are not only functional but also expressive and sustainable.
The Catalyst for Change
Multiple factors catalyzed this transformation: climate change awareness increased the demand for sustainable building practices; globalization accelerated the exchange of ideas and design innovation; rapid technological development, such as Building Information Modeling (BIM) and smart materials, revolutionized construction methods. The rise of digital culture also fostered a reimagining of how design interfaces with human experience.
Geography
Global Spread and Regional Adaptations
The influence of modern architectural concepts is visible worldwide, from the skyscrapers of Dubai to eco-friendly urban cores in Scandinavia. Urban centers in Asia, Europe, and North America are pioneering smart city initiatives, integrating IoT (Internet of Things) and AI (Artificial Intelligence) to optimize urban infrastructure. Geographic diversity plays a crucial role; arid regions emphasize passive cooling and water efficiency, while coastal cities prioritize resilience against climate change through elevated structures and flood defenses.
Urban Planning and Land Use
The push towards high-density, mixed-use developments facilitates vibrant, sustainable communities. Green belts and urban parks are incorporated into dense cityscapes to balance growth with ecological preservation, reflecting an enlightened approach to urban planning informed by a renaissance of holistic design thinking.
Society & Culture
Design for Humanity and Inclusivity
Modern architecture champions inclusivity, accessibility, and cultural expression. Adaptive reuse projects preserve historical architecture while integrating contemporary needs, fostering a dialogue between past and present. Public spaces are designed to encourage social interaction and cultural engagement, reflecting societal shifts toward communal experiences.
Technology as a Cultural Force
The infusion of virtual reality (VR), augmented reality (AR), and digital fabrication techniques influence not only construction practices but also cultural perceptions of space. These tools allow architects to craft immersive environments, expanding the boundaries of traditional aesthetics and functionality.
Economy & Trade
Green Economy and Sustainable Investment
Investment in sustainable infrastructure fuels economic growth, with green buildings offering lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact. The market for innovative materials — such as self-healing concrete, recycled composites, and transparent aluminum — is booming, driving economic opportunities and global trade channels.

Construction Industry Revolution
Prefabrication, modular construction, and 3D printing are making building more efficient and adaptable. Digital supply chains optimize material flow, reducing waste and costs. This economic shift accelerates the realization of ambitious urban projects and reshapes global construction markets.
Military & Technology
Smart Infrastructure and Defense
Technologies initially developed for military applications, such as drone surveillance and advanced materials, are now integral to civilian architecture and urban design. Secure, resilient structures incorporate sensor networks for real-time monitoring, enhancing safety and responding to environmental threats.
Technological Advancements in Construction
Innovations like robotics, autonomous construction vehicles, and AI-driven design algorithms are streamlining the building process. These advancements enable precision, reduce labor dependency, and facilitate complex structures that were previously unattainable.
Governance & Law
Regulation and Policy Shifts
Governments worldwide are adopting policies to promote sustainable growth—mandating energy efficiency standards, incentivizing green building certifications such as LEED and BREEAM, and facilitating public-private partnerships for urban redevelopment.
Urban Governance and Community Engagement
Participatory planning processes and transparent governance models ensure that development aligns with community needs, fostering civic trust and inclusivity. Legal frameworks support innovation while safeguarding ecological and social interests.
Archaeology & Sources
Contemporary design draws lessons from archaeological insights regarding sustainable resource utilization, spatial organization, and cultural symbolism. Sources include digital archives, modern excavation reports, and interdisciplinary collaborations, providing context and inspiration that bridge past and future.
Timeline
- 2000 – Introduction of Building Information Modeling (BIM) revolutionizes design process.
- 2005 – Rise of energy-efficient green building certifications gains global traction.
- 2010 – Emergence of smart city initiatives integrating IoT and AI.
- 2015 – Development of innovative, sustainable construction materials like self-healing concrete.
- 2020 – Pandemic accelerates focus on health-conscious, adaptable architecture.
- 2023 – Integration of AI-driven design tools and 3D printing in mainstream construction.
Debates/Controversies
Discussions persist around the ecological footprint of new developments, gentrification implications, and the equitable distribution of technological benefits. Ethical dilemmas regarding automation, data privacy, and the cultural implications of digital design tools are ongoing debates shaping policy and practice.
Conclusion
The modern renaissance in architecture signifies a profound shift towards holistic, sustainable, and technologically integrated design. As cities continue to grow and face complex challenges, these emerging concepts promise resilient, adaptive spaces that honor our cultural history while embracing the innovations that will define tomorrow’s urban landscapes.